Stakeholders and Materiality
Mitsui Kinzoku Group is committed to practicing management that integrates sustainability in order to continue creating value over the long term. We have identified major stakeholders as well as material issues (materiality) to promote the integrated thinking-based management efficiently.
Stakeholder identification
Mitsui Kinzoku Group has identified major stakeholders in accordance with the eight criteria of ISO 26000. The major stakeholders are determined as highly likely to be affected by our business activities economically, environmentally, and socially. The earth environment is considered as being one of our major stakeholders. The SDGs indicate the common social and environmental issues which these multiple stakeholders are facing.
Stakeholder mapping along the value chain
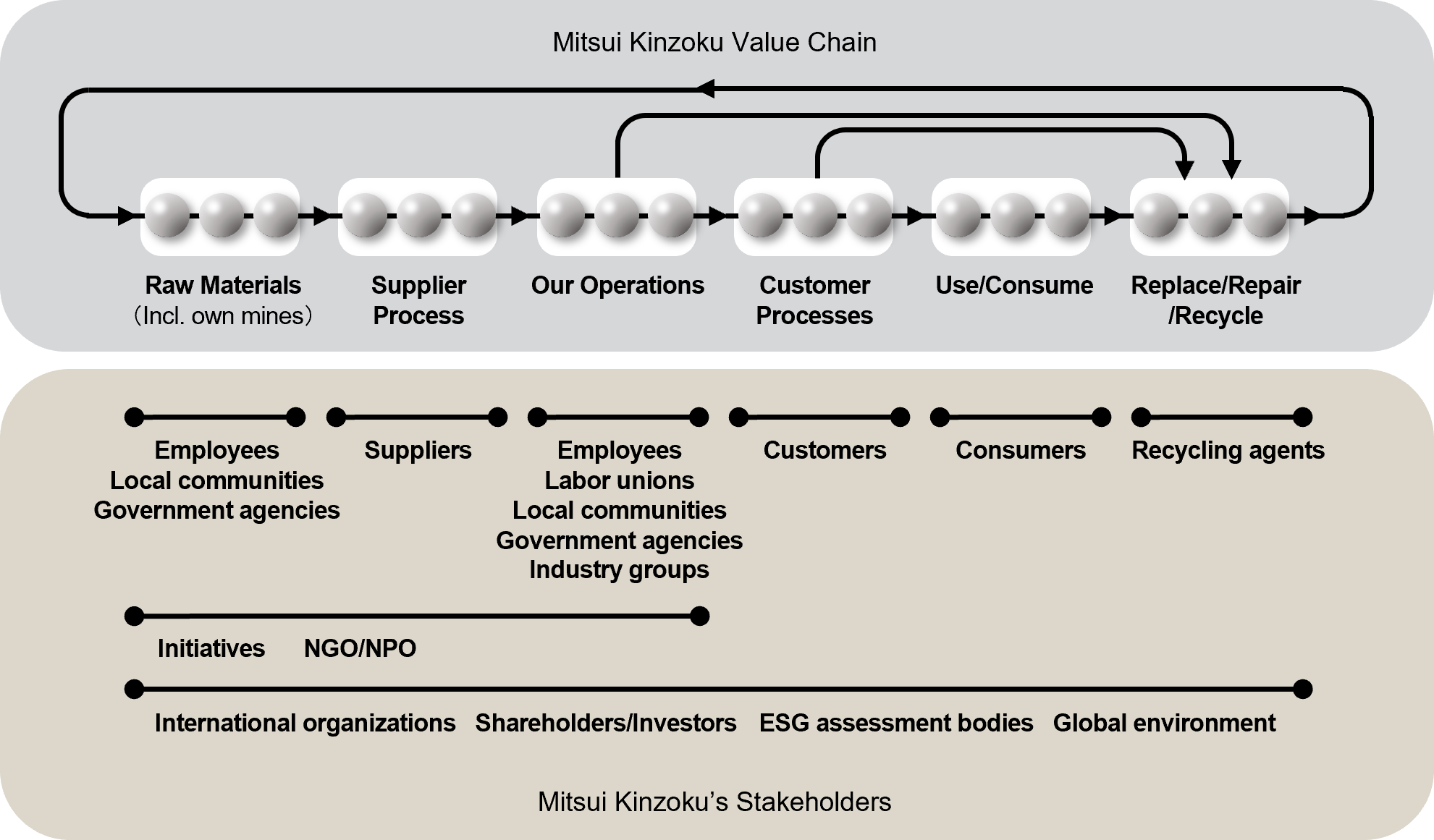
Stakeholder Engagement
We carry out engagement activities with major identified stakeholders through various opportunities.
As for responsible mineral sourcing, we support the RMI program for gold, tantalum and tin, the LBMA for silver, and the LME for zinc, lead and copper.
To promote responsible sourcing in general, we participate in the Responsible Minerals Trade Working Group of the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association(JEITA)as a member to support RMI’s activities.
We also respect the Responsible Business Alliance(RBA) code of conduct in internal activities and those undertaken in supply chains.
Identification, assessment and review of materiality
Among environmental and social issues raised by the major stakeholders, we identify material issues i.e. materiality. The materiality can pose ESG risks that affect us financially or can turn out to be our business opportunities that may profit us by offering solutions for the issues through our business or in our value chains. By responding to risks and opportunities presented by the materiality, we will implement the integrated management strategy built on the two pillars of business and social responsibility.
Identification FY2016
-
STEP1
Identify issues based on the seven core subjects of ISO 26000 in reference to the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) guidelines (G4) and SDGs.
-
STEP2
Narrow down the candidates based on the questionnaires and results by ESG assessment bodies.
-
STEP3
Based on identified stakeholders, sort out and analyze their major requests and expectations.
-
STEP4
Step4 image
By taking into account both the materiality for stakeholders and that for Mitsui Kinzoku, map the candidate issues identified in Step 2. The CSR Committee then identifies 28 material issues for Mitsui Kinzoku, and they are approved by the Executive Council and the Board of Directors.
Assessment FY2017
For a future intention to integrate solutions for social and environmental issues into management strategies, we assessed the materiality, whether it is a risk or an opportunity, from the ESG perspective of the GRI standards, and linked the materiality to SDGs.
Assessment FY2018
In FY2018, we conducted the materiality assessment again in connection to the new medium-term management plan (19 Medium Plan). This assessment was conducted in terms of what will have influence on our long-term value creation ability. This assessment used the SASB*1 standard and the ESG general standards*2 offered by Amundi, the largest asset management company in Europe. The SASB standard lists the disclosure items and indexes that have particular impact on a company’s finances by each industry type and ESG issue. The ESG general standards comprised of 15 factors helps to evaluate the level of influence and probability of impact on the company’s value.
Utilizing these standards, we extracted materiality from the items required by ESG investment that may have particular impact on our business model and finances. We grouped them as “materiality issues in the areas of responsibility that relate to the social & relationship and the natural capital”.
(For the SASB standards by industrial sectors, we referred to the Metals & Mining category in the Extractives & Minerals Processing Sector in order to incorporate the risks that are unique to mining.)
*1 SASB Sustainability Accounting Standards Board
*2 Amundi ESG general standard
<Reference> Amundi Japan (2018) "Introduction to ESG investment that will change society", Nikkei Publishing Inc.
Review FY2019
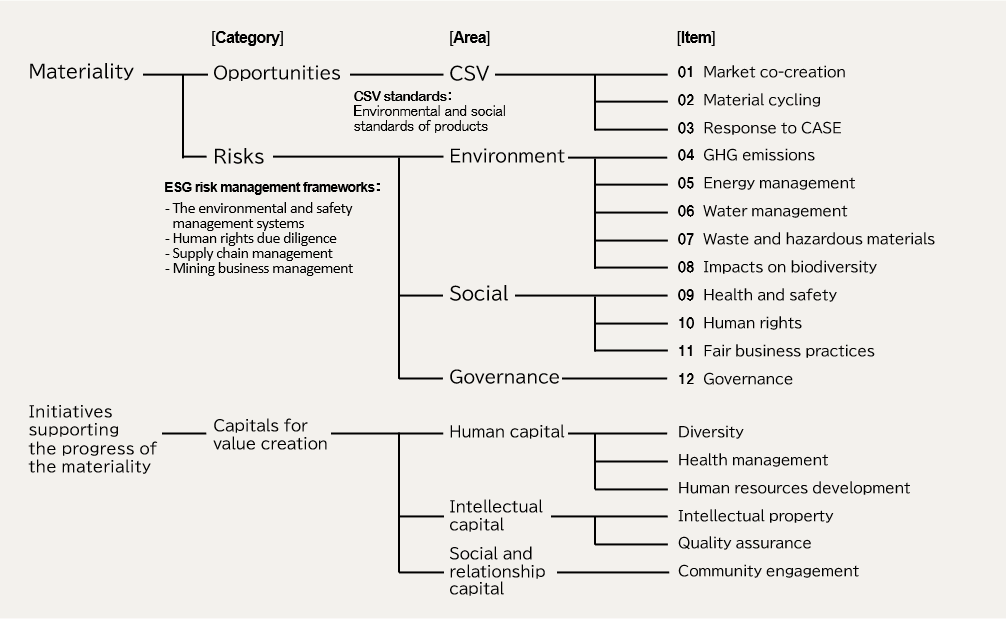
In FY2019, we reviewed our materiality for 2024 in order to implement our integrated management strategy built on the two pillars of business and social responsibility. The revised materiality comprises three items as opportunities and nine items as risks based on two perspectives: opportunities for our businesses that may help solve the raised issues and ESG risks that may affect us financially which are regarded as initiatives to fulfill our social responsibility. We have also selected six additional items from the capital perspective as initiatives to support the efforts on materiality.
-
STEP1
Enumerated a wide range of economic, environmental, and social issues from a long-term perspective
Ref. The SDGs, the United Nations Global Compact, the GRI Standards and ISO 26000 as issues raised by international organization like the UN and NPOs
-
STEP2
Selected issues that are likely to have a long-term impact on our business and value chains
Ref. The Management Philosophy, the Code of Conduct, the 19 Medium Plan
-
STEP3
Determined the level of materiality for each issue selected in 2 above according to the degree of the major stakeholders’ expectations and needs regarding our business and their impacts
Ref.
<International organizations> OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Business Conduct
<Investors> The SASB standards, the ESG general standards by Amundi
<Industrial initiatives> The RBA Code of Conduct (Customer/Supplier), ICMM 10 Principles, the Charter of Corporate Behavior by Keidanren
-
STEP4
Determined the level of materiality for each issue selected in 2 above at the CSR Committee according to the degree of impact on our business model and finances
Ref. The 19 Medium Plan, the Code of Conduct, the Environmental Action Plan, the Human Rights Standards, the procurement policy
-
STEP5
STEP5 image
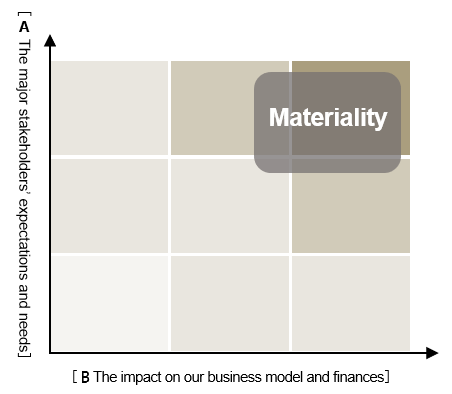
Mapped the issues on the two axes of 3 and 4 above (see the right graph) and identified the ones in the shaded area as material issues
-
STEP6
Divided the material issues, based on the integrated management strategy of business and social responsibility, into ones that may pose ESG risks (social responsibility) that are likely to affect us financially and into ones that can turn out to be business opportunities
Ref. The International Integrated Reporting Framework, the SASB standards
-
STEP7
Classified the issues mapped in the lighter-colored parts in the graph into a set of issues that supports the progress on the material issues
-
STEP8
Received approval from the Board of Directors for the materiality of ESG risks and business opportunities
Commitment FY2020
In FY2020, the CSR Committee led discussions on commitments, targets (KPIs), and plans of each revised materiality item. At the departments responsible for each materiality item, we developed respective lists of issues surrounding the items, examined stakeholders’ expectations and requirements based on the approximately 750 issues selected in Step 2 and the mapping in Step 5. Then, we discuss the Group’s visions for 2024 and incorporated into our commitments and set targets (KPIs) as the indicators to achieve them. The annual plans until FY2023 define more details on how to achieve these targets.
PDCA FY2021
In FY2021, the departments responsible for each materiality item put plans into practice to achieve the commitments and targets (KPIs) set in the previous fiscal year. By the end of the fiscal year, we confirmed the results of initiatives and plans for FY2022. The progress of the entire Group was gathered and reported at the CSR Committee.
PDCA FY2022
In FY2022, the departments responsible for each materiality item carried out initiatives according to the annual plans. At the end of the fiscal year, results for each item were confirmed and plans for FY2023 were reviewed in consideration of changes in the external environment and major stakeholders’ interests. Information on the progress of the Group was gathered and reported to the CSR Committee.
PDCA FY2023
In FY2023, the departments responsible for each materiality item carried out initiatives according to the annual plans. At the end of the fiscal year, results for each item were confirmed and plans for FY2024 were reviewed in consideration of changes in the external environment and major stakeholders’ interests. Information on the progress of the Group was gathered and reported to the CSR Committee.
Materiality
The materiality of opportunities and risks comprises three items as opportunities and nine items as risks based on two perspectives: opportunities for our businesses that may help solve the raised issues and ESG risks that may affect us financially. We have also selected six additional items from the capital perspective as initiatives to support the efforts on materiality.
Integrated Report Stakeholders and Materiality [PDF:634KB]
Target, progress and performance of Material Issues
Mitsui Kinzoku Group has compiled commitments, targets (KPIs), and plans of each materiality item in “Mitsui Kinzoku Group Sustainability Initiatives”. Since FY2021, we have been running the PDCA cycle and managing the group-wide progress.
Integrated Report Mitsui Kinzoku Group Sustainability Initiatives [PDF:628KB]